
- hematology home
- immunology home
- signs and symptoms
- investigations
- conditions and diseases
Section Links
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is the splace between the bone cortex. It contains bone trabeculae and blood vessels. It is the primary site of hematopoiesis in adults.
- structure
- hematopoietic cells
- hematopoietic growth factors
- bone marrow microenvironment
- factors affecting responsiveness
Bone Marrow Structure
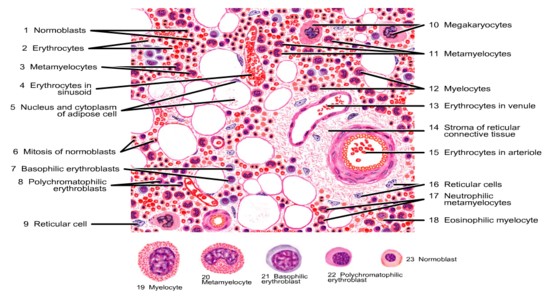
Bone marrow contains vascular sinusoids with a network of reticular cells and fibres in close proximity. The marrow synctitium is designed to provide developing cells with a nutrient-rich environment. Cells lining the sinusoids regulate the exit of cells from the marrow.
<<PIC of SINUSOIDS>>
Hematopoietic Cells
myeloblasts 0-13%
prom 3-12
myelocytes 2-13%
bands/neutrophils 23-45%
eosinophils 0.3-4%
lymphocytes 0-0.4
monocytes
monoblasts 13-38%
myeloid : erythroid precursors is normally 2-4 : 1
Hematopoietic Growth Factors
Bone Marrow Microenvironment
extracellular matrix
The ECM allows attachment of hematopoietic cells and contributes signals controlling proliferation and differentiation. Components include:
- fibronectin
- laminin
- collagen
ECM also regulates HSC location, facilitating interaction with stromal cells.
stromal cells
stromal cells provide physical support for hematopoietic cells and produce growth factors/cell surface proteins that influence differentiation.
- fibroblasts
- osteoblasts
- macrophages
- endothelial cells
- adipocytes
Factors Affective Responsiveness